Cord Hosting has partnered with
Katharion the industry leader for detecting junk email. The result
of thousands of hours of development and Katharionís experience
from processing billions of messages Katharion has created techniques
for spam and virus detection in combination with a variety of next-generation
approaches for message analysis that provide effective and successful
filtering results.
As a managed service provider Katharion is compatible with any email
system and can be implemented rapidly. At the same time, Katharionís
customizable management interface and innovative features such
as one-click whitelisting assure that the solution is both simple
to deploy and extremely easy to maintain.
Through a simple DNS
change, email is automatically protected, without any hardware,
software, or configuration changes for the customer. The change
of the 'MX' record (mail exchanger) for your domain point to Katharion's
systems. After that change has been made, your email will be redirected
through Katharionís filters before being automatically delivered
to your mail server. |
| |
 |
| |
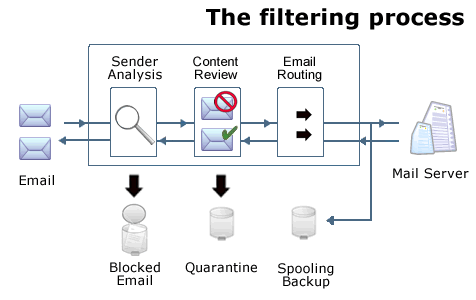
| Message Handling |
| |
|
|
|
| Drop detected spam: An
aggressive approach that reduces a customerís network bandwidth
requirements and mail server load. Due to Katharion's extremely
low percentage of "false positives" it is very rare that a legitimate
email message will be dropped. |
| |
| Tag and forward detected spam:
with a modified subject line, incoming email can be automatically
directed to a specific folder in each userís email program for periodic
review and/or deletion. |
| |
| Redirect detected spam: junk
mail can be directed to an alternative address, e.g., spam@example.com. |
| |
| Quarantine: Junk messages
are redirected to individual web-mail quarantine accounts that can
be reviewed at any time by end users. The most common choice of
larger businesses and ISPs, this approach reduces bandwidth requirements
and mail server load for customers while providing complete assurance
that no legitimate message will ever be lost. |
| |
| In addition to these basic choices
which be configured by person, by group, by domain, or by company,
customers can opt to receive periodic message digests, which
provide each user a summary list of the junk email received for
them. |
| |
|
|
|
| Message Analysis |
| |
 |
An extensive, continually
updated Heuristic Rule Set that encompasses message headers,
body text, and other characteristics of both English-language and
non-English messages |
 |
Public and Private
Blacklists of mail servers, relays, or networks known to be
used by spammers |
| |
|
|
|
 |
Extensive
URI Databases of unique elements such as URLs, phone numbers,
and physical addresses known to be used by spammers |
 |
Extensive
URI Databases of unique elements such as URLs, phone numbers,
and physical addresses known to be used by spammers l |
| |
|
|
|
 |
A self-learning
Bayesian Engine that analyzes patterns of phrases in messages,
and assigns mathematical probabilities for the presence of those
phrases in junk mail versus legitimate mail |
 |
Incorporation
of Domain History and Reputation to increase the accuracy of
blacklists and URI databases |
| |
|
|
|
 |
Real-Time Message
Source Analysis to assess whether an increased volume of mail
flow is simply a legitimate high-volume mailing, or the result of
a spammer hijacking or the use of a Ďzombieí network |
 |
User-Based Message
Profiling that allows for refinement of message scoring for each
user based on a history of his or her message traffic |
| |
|
|
|
 |
Customizable whitelists
and blacklists which can be applied on an account-wide, organization-wide,
domain-wide, or user-specific basis |
 |
Message Fingerprinting
to compare email signatures to frequently-updated public and internal
databases of known spam messages |
| |
|
|
|
 |
Authenticity Checks
including detailed header analysis |
|
|
| |
|
|
|





